如何使用C++通过thrift访问HBase进行操作
前言
上周六,接了一个紧急任务,说实现使用 C++ 访问 HBase 进行操作。说是用 thrift 来实现。对于 C++ 来说,我真的是门外汉,但需求如此,皱着眉头也要把它实现。好歹在同事的帮助下,也是实现了 demo 示例,现在就把这两天的成果分享给大家。
版本
HDP:2.6.4.0
HBase:1.1.2
一、安装编译thrift
1. 准备工作
使用 yum 安装 Development Tools :
1 | yum -y groupinstall "Development Tools" |
thrift 编译依赖于下面的工具,使用 yum 安装:
1 | yum -y install automake libtool flex bison pkgconfig gcc-c++ boost-devel libevent-devel python-devel ruby-devel zlib-devel openssl-devel |
2. 下载thrift安装包
为了生成依赖类库 /usr/local/include/thrift/ 和 /usr/local/lib/ ,需要下载 thrift 源码包。本文使用 thrift 0.8.0 版本,通过以下地址下载后并解压。
1 | cd /usr;wget http://archive.apache.org/dist/thrift/0.8.0/thrift-0.8.0.tar.gz |
3. 编译thrift
1 | cd /usr/thrift-0.8.0 |
命令执行完毕后,如下图所示:
编译 thrift ,执行如下命令:
1 | make && make install |
命令执行完毕后,如下图所示:
至此,thrift 0.8.0 就编译完成了。可执行 thrift -version 查看版本。
4. 检查相关文件是否存在
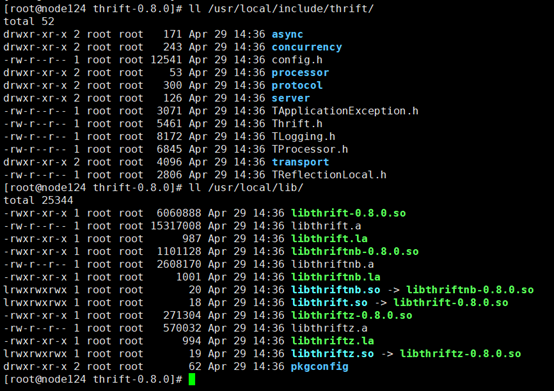
thrift编译成功后,会在 /usr/local/include/thrift/ 和 /usr/local/lib/ 目录下生成相关文件,用于后面使用 g++ 工具编译 cpp 文件。如下图所示:
二、代码示例
1. 开启HBase thrift2
首先需要确保 HBase thrift2 服务正常运行。执行如下命令启动 HBase thrift2 服务:
1 | /usr/hdp/2.6.4.0-91/hbase/bin/hbase-daemon.sh start thrift2 |
服务开启的默认端口号为 9090 ,可执行 netstat -ntlp | grep 9090 检测 thrift2 是否成功启动。
2. 生成c++相关文件
1 | 进入到hbase源码目录 |
gen-cpp 目录下的文件列表如下图所示:

3. 编写客户端代码
创建 HbaseClient.cpp 文件(名称可自定义),向 hbase_test 表中插入一条数据,并打印指定 rowkey 的一行数据。代码内容如下所示:
1 |
|
4. 生成可执行的文件HbaseClient
使用 g++ 工具编译客户端代码,在 HbaseClient.cpp 所在的目录下执行以下命令:
1 | g++ -DHAVE_NETINET_IN_H -o HbaseClient -I/usr/local/include/thrift -I./gen-cpp -L/usr/local/lib HbaseClient.cpp ./gen-cpp/hbase2_types.cpp ./gen-cpp/hbase2_constants.cpp ./gen-cpp/THBaseService.cpp -lthrift -g |
命令参数说明:
- -DHAVE_NETINET_IN_H:该参数解决编译时使用定义的文件内容。
- -I/usr/local/include/thrift与-I./gen-cpp:g++会先在当前目录查找你所制定的头文件,如果没有找到,会回到缺省的头文件目录查找。使用-I参数指定目录,g++会先在你指定的目录中查找,然后再按常规的顺序查找。
- -o HbaseClient:编译后输出HbaseClient文件。缺省状态下,编译后输出的文件为a.out。
- -L/usr/local/lib:编译的时候,指定搜索库的路径。
- -g:指示编译器,在编译时,产生调试信息。
5. 创建HBase表
在运行客户端之前,我们需要创建一个 hbase_test 表。创建表命令如下所示:
进入 HBase shell 命令行:
1 | hbase shell |
创建 hbase_test 表:
1 | create 'hbase_test', {NAME => 'info'} |
可执行 exit 命令退出命令行。
6. 运行客户端
可通过如下命令运行 HbaseClient 客户端:
1 | 在HbaseClient文件所在的当前目录下执行 |
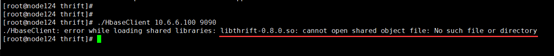
会出现错误:libthrift-0.8.0.so: cannot open shared object file。如下图所示:
解决方法:
需要配置环境变量。将export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/lib添加至/etc/profile文件中,如下图所示:
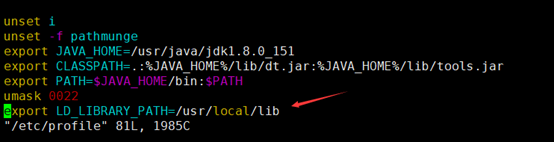
最后,执行 source /etc/profile 命令,使环境变量立即生效。
再执行 ./HbaseClient <thrift2_ip> <thrift2_port> 命令试试。
三、总结
1、在 /usr/hdp/2.6.4.0-91/hbase/include/thrift 目录下有两个文件,为 hbase1.thrift 和hbase2.thrift ,分别对应的thrift 1服务与thrift 2服务。本文采用 thrift 2 连接 HBase 数据库对表进行数据插入与读取操作。
2、使用 thrift --gen cpp hbase2.thrift 命令生成服务端相关代码。
3、在编写客户端文件时,通过 THBaseService.h 文件访问 HBase 服务端,使用 hbase2.thrift 文件内提供的方法对 HBase 数据库进行操作。
四、参考资料
我将这两天搜集的资料,觉得不错的列在下面,也方便继续深入的人查阅。
- https://www.cnblogs.com/yhp-smarthome/p/8982758.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/zhaoxd07/p/5387215.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/u013913435/article/details/77119647
- 有些方法的描述:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-31429829-id-5785871.html?tdsourcetag=s_pctim_aiomsg
- 根据这个实现:https://blog.csdn.net/yinzhiqing/article/details/51943370
- https://blog.csdn.net/happyrabbit456/article/details/8116305
- 看着不错,但没具体参照实现:https://blog.csdn.net/zhijiayang/article/details/46334707
点关注,不迷路
好了各位,以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,能看到这里的人呀,都是人才。
白嫖不好,创作不易。各位的支持和认可,就是我创作的最大动力,我们下篇文章见!
如果本篇博客有任何错误,请批评指教,不胜感激 !
原文作者: create17
原文链接: https://841809077.github.io/2019/04/29/HBase/如何使用C-通过thrift访问HBase进行操作.html
版权声明: 转载请注明出处(码字不易,请保留作者署名及链接,谢谢配合!)




